Peptic ulcer
Peptic ulcer
Overview
-
Ulcers
Peptic ulcers include:
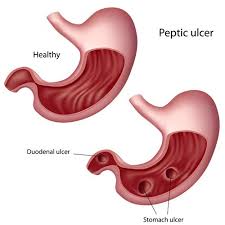
- Gastric ulcers that occur on the inside of the stomach
- Duodenal ulcers that occur on the inside of the upper portion of your small intestine (duodenum)
Symptoms
- Burning stomach pain
- Feeling of fullness, bloating or belching
- Fatty food intolerance
- Heartburn
- Nausea
Nearly three-quarters of people with peptic ulcers don't have symptoms.
Less often, ulcers may cause severe signs or symptoms such as:
- Vomiting or vomiting blood — which may appear red or black
- Dark blood in stools, or stools that are black or tarry
- Trouble breathing
- Feeling faint
- Nausea or vomiting
- Unexplained weight loss
- Appetite changes
When to see a doctor
See your doctor if you have the severe signs or symptoms listed above. Also see your doctor if over-the-counter antacids and acid blockers relieve your pain but the pain returns.Causes
Peptic ulcers occur when acid in the digestive tract eats away at the inner surface of the stomach or small intestine. The acid can create a painful open sore that may bleed.Your digestive tract is coated with a mucous layer that normally protects against acid. But if the amount of acid is increased or the amount of mucus is decreased, you could develop an ulcer. Common causes include:
- A bacterium. Helicobacter pylori bacteria commonly live in the mucous layer that covers and protects tissues that line the stomach and small intestine. Often, the H. pylori bacterium causes no problems, but it can cause inflammation of the stomach's inner layer, producing an ulcer.
It's not clear how H. pylori infection spreads. It may be transmitted from person to person by close contact, such as kissing. People may also contract H. pylori through food and water.
- Regular use of certain pain relievers. Taking aspirin, as well as certain over-the-counter and prescription pain medications called nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can irritate or inflame the lining of your stomach and small intestine. These medications include ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve, Anaprox, others), but not acetaminophen (Tylenol).
Peptic ulcers are more common in older adults who take these pain medications frequently or in people who take these medications for osteoarthritis.
- Other medications. Taking certain other medications along with NSAIDs, such as steroids, anticoagulants, low-dose aspirin, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), alendronate (Fosamax) and risedronate (Actonel), can greatly increase the chance of developing ulcers.
Risk factors
In addition to taking certain pain medications, including aspirin, you may have an increased risk of peptic ulcers if you:- Smoke. Smoking may increase the risk of peptic ulcers in people who are infected with H. pylori.
- Drink alcohol. Alcohol can irritate and erode the mucous lining of your stomach, and it increases the amount of stomach acid that's produced.
- Have untreated stress.
- Eat spicy foods.
Complications
Left untreated, peptic ulcers can result in:- Internal bleeding. Bleeding can occur as slow blood loss that leads to anemia or as severe blood loss that may require hospitalization or a blood transfusion. Severe blood loss may cause black or bloody vomit or black or bloody stools.
- Infection. Peptic ulcers can eat a hole through (perforate) the wall of your stomach or small intestine, putting you at risk of serious infection of your abdominal cavity (peritonitis).
- Obstruction. Peptic ulcers can lead to swelling, inflammation or scarring that may block passage of food through the digestive tract. A blockage may make you become full easily, vomit and lose weight.
Prevention
You may reduce your risk of peptic ulcer if you follow the same strategies recommended as home remedies to treat ulcers. It may also be helpful to:- Protect yourself from infections. It's not clear just how H. pylori spreads, but there's some evidence that it could be transmitted from person to person or through food and water.
You can take steps to protect yourself from infections, such as H. pylori, by frequently washing your hands with soap and water and by eating foods that have been cooked completely.
- Use caution with pain relievers. If you regularly use pain relievers that increase your risk of peptic ulcer, take steps to reduce your risk of stomach problems. For instance, take your medication with meals.
Work with your doctor to find the lowest dose possible that still gives you pain relief. Avoid drinking alcohol when taking your medication, since the two can combine to increase your risk of stomach upset.
If you need to take a pain medication associated with ulcers, you may need to also take additional medications such as an antacid, a PPI, an acid blocker or cytoprotective agent.


Comments
Post a Comment